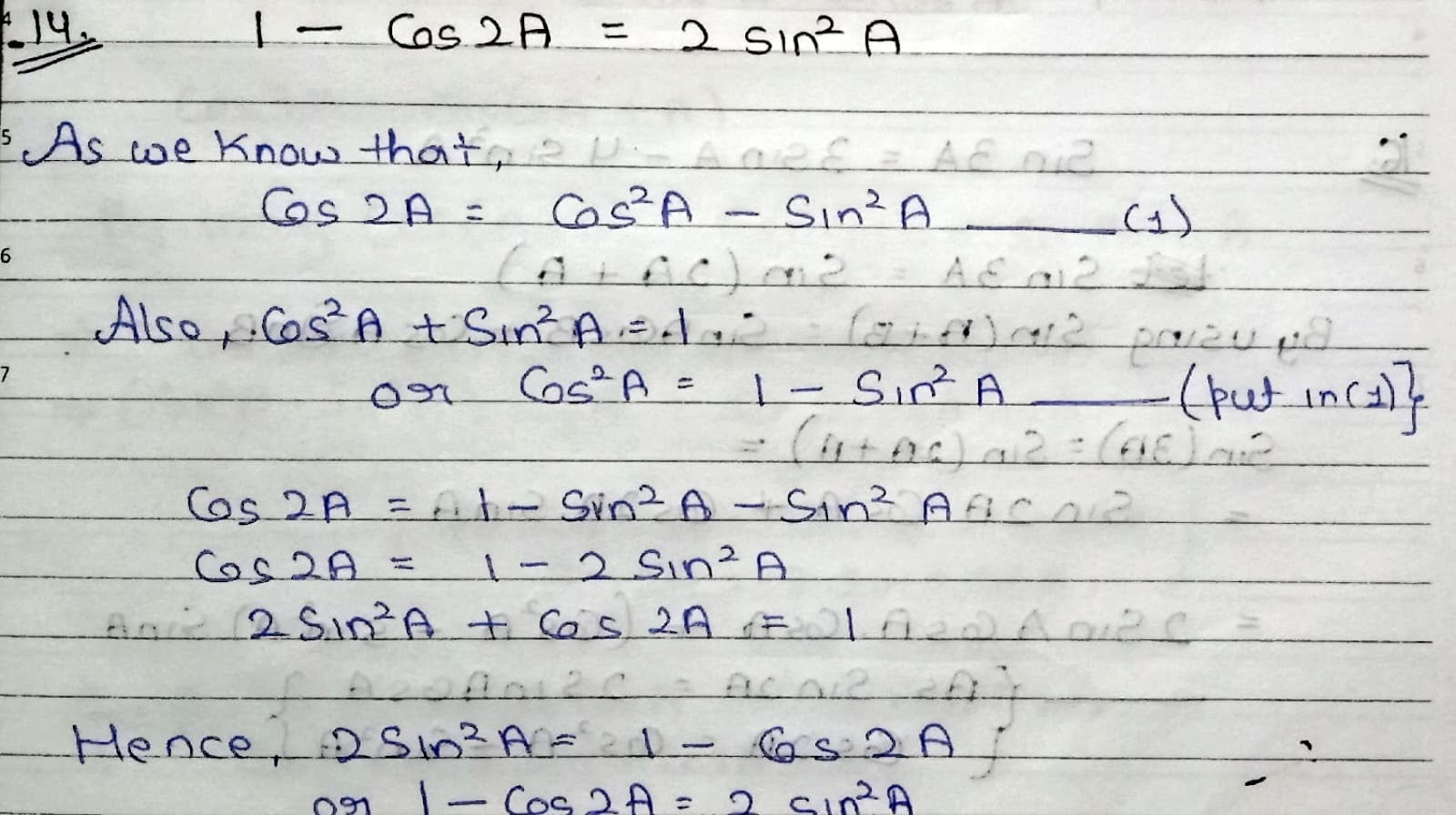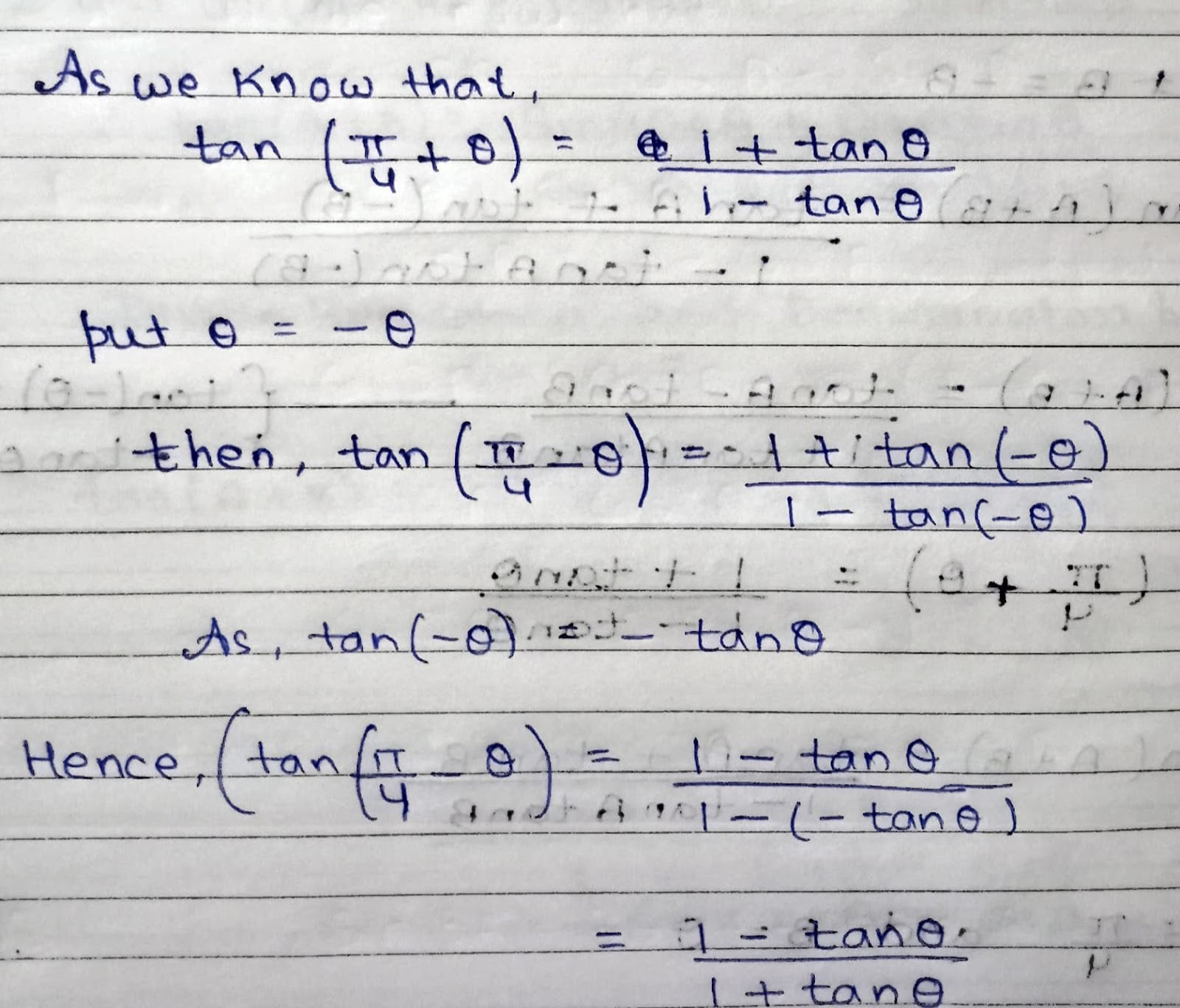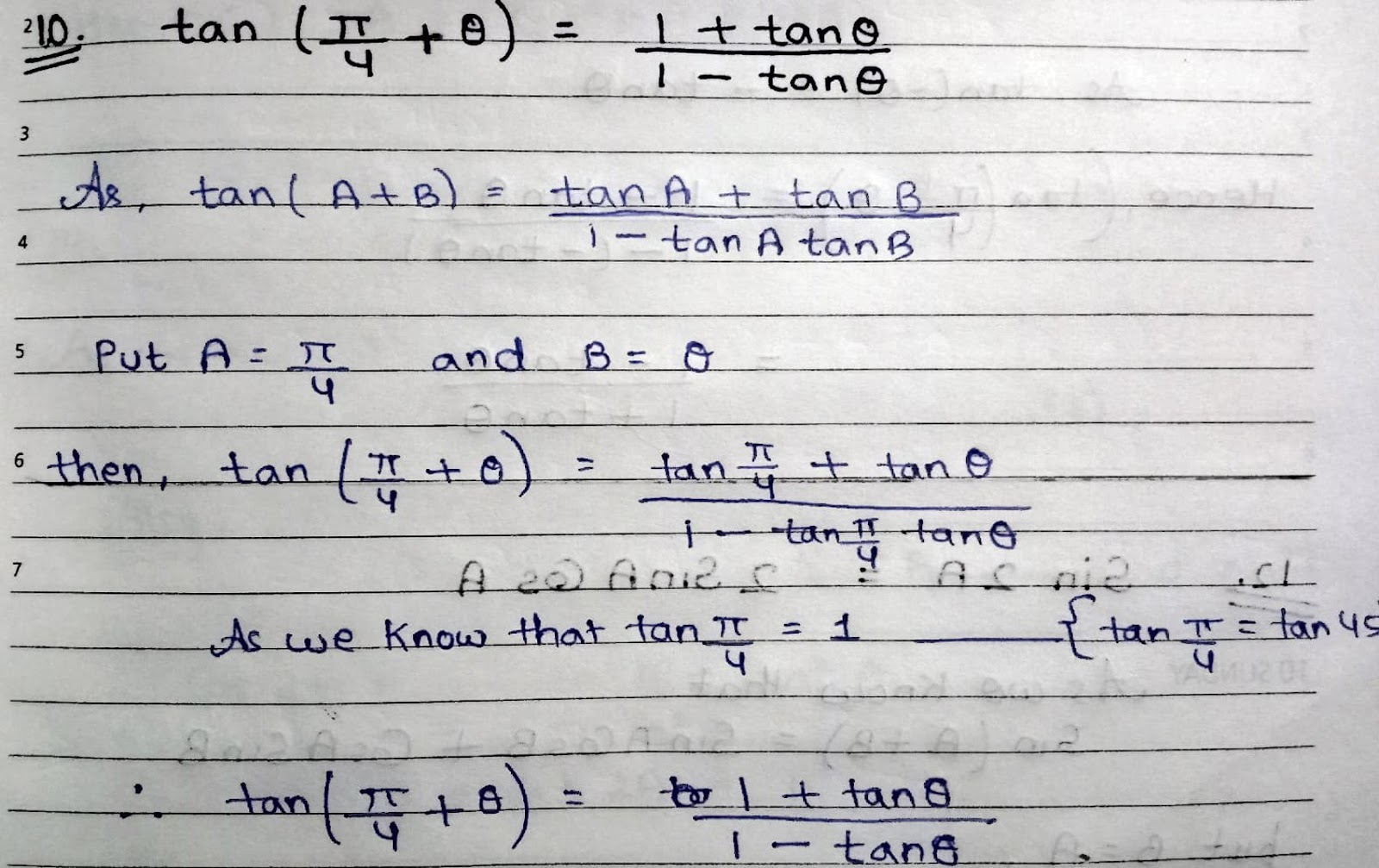How 1 - Cos2A = 2 sin²A? As we know that, Cos(2A) = Cos²A - Sin²A.........(1) ........👉{ Cos(2A) = Cos²A - Sin²A } also, Sin²A + Cos²A = 1 or Cos²A = 1- Sin²A......(2) ...............👉{ How Sin²θ + Cos²θ = 1?? } put eq. (2) into eq.(1) Cos(2A) = 1 - Sin²A - Sin²A Hence, Cos(2A) = 1 - Sin²A also, 1 - Cos2A = 2 sin²A If angle(ϴ) is halved, then, CosA = 1 - Sin²(A/2) or 1 - CosA = 2 sin²(A/2)